What we will build
At the end of this tutorial you will build a simple serverless function in Python running on Digital Ocean Serveless Functions.
The function will be able to calculate distance of a path between points on the Earth given their latitude and longitude. We will also call the function using cURL to test it.
Prerequisites
- Basic Python knowledge
- Digital Ocean account
- Digital Ocean CLI
Checking if everything is installed
Let’s check if we are ready to use all the tools we need for this tutorial.
doctl
doctl version
# Example output: `doctl version 1.111.0-release`
doctl serverless
doctl serverless status
If you have problems with doctl serverless, please follow the steps provided by the CLI. You may need to install the serverless plugin and create a namespace for the serverless functions.
Setting up the project (locally)
Let’s create our project.
doctl serverless init --language python world-map-path-python
Go to the folder with the project and open it in your favorite editor.
First thing will be creating editing project.yaml file.
You can pretty much cut everything out and leave only the packages, name, functions and runtime fields.
Finally the file should look like this:
packages:
- name: world-map-path
functions:
- name: distance
runtime: python:default
The main name fields correspond to the names of directories that we will create right now.
The folder structure should look like this (create an empty __main__.py file in the distance directory):
.
├── packages
│ └── world-map-path
│ └── distance
│ └── __main__.py
└── project.yml
Now the fun part begins, which is writing the code for the function.
For the calculations of the distance between two points on the Earth we will use the geopy library.
Here is a quick overview of the code that we will be using:
- We will import the
geodesicfunction from thegeopy.distancemodule. This will allow us to easily calculate the distance between two points on the map. - There will be only one function -
mainwhich will take theargsdictionary as an argument. Theargsdictionary will contain thepointslist with the latitude and longitude of the points. The arguments are provided by the functionality of the serverless functions. - We will iterate over the
pointslist and calculate the distance between each pair of points. We will sum all the distances and return the total distance in meters. - The function will return a dictionary with the
body,statusCodeandheadersfields. It is required to return it in this form to allow connecting via cURL.
The code for the __main__.py file should look like this:
from geopy.distance import geodesic
def main(args):
points = args.get("points", [])
total_distance = 0.0
for i in range(len(points) - 1):
start_point = points[i]
end_point = points[i + 1]
distance = geodesic(start_point, end_point).meters
total_distance += distance
return {
"body": {"distance": total_distance},
"statusCode": 200,
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
}
We also need to provide the requirements.txt file with the geopy library and file which will tell Digital Ocean how to install the dependency.
requirements.txt
geopy
build.sh
#!/bin/bash
set -e
virtualenv --without-pip virtualenv
pip install -r requirements.txt --target virtualenv/lib/python3.9/site-packages
You may also need to add the execution permission to the build.sh file:
chmod +x build.sh
The final structure of the project should look like this:
.
├── packages
│ └── world-map-path
│ └── distance
│ ├── __main__.py
│ ├── build.sh
│ └── requirements.txt
└── project.yml
Deploying the function
Now we are ready to deploy the code to Digital Ocean.
doctl serverless deploy . --remote-build
At the end of the response from the CLI you should see:
...
Deployed functions ('doctl sls fn get <funcName> --url' for URL):
- world-map-path/distance
Let’s run the command to get the URL of the function:
doctl sls fn get world-map-path/distance --url
The command should print the url to the function. Copy it because we will use it in the next step.
Testing the function
Final step is testing if the function works correctly.
We will do this by calling the function using cURL.
We will test distance from Berlin to Warsaw.
According to the world-map-path app, it should take around 510-520 km.
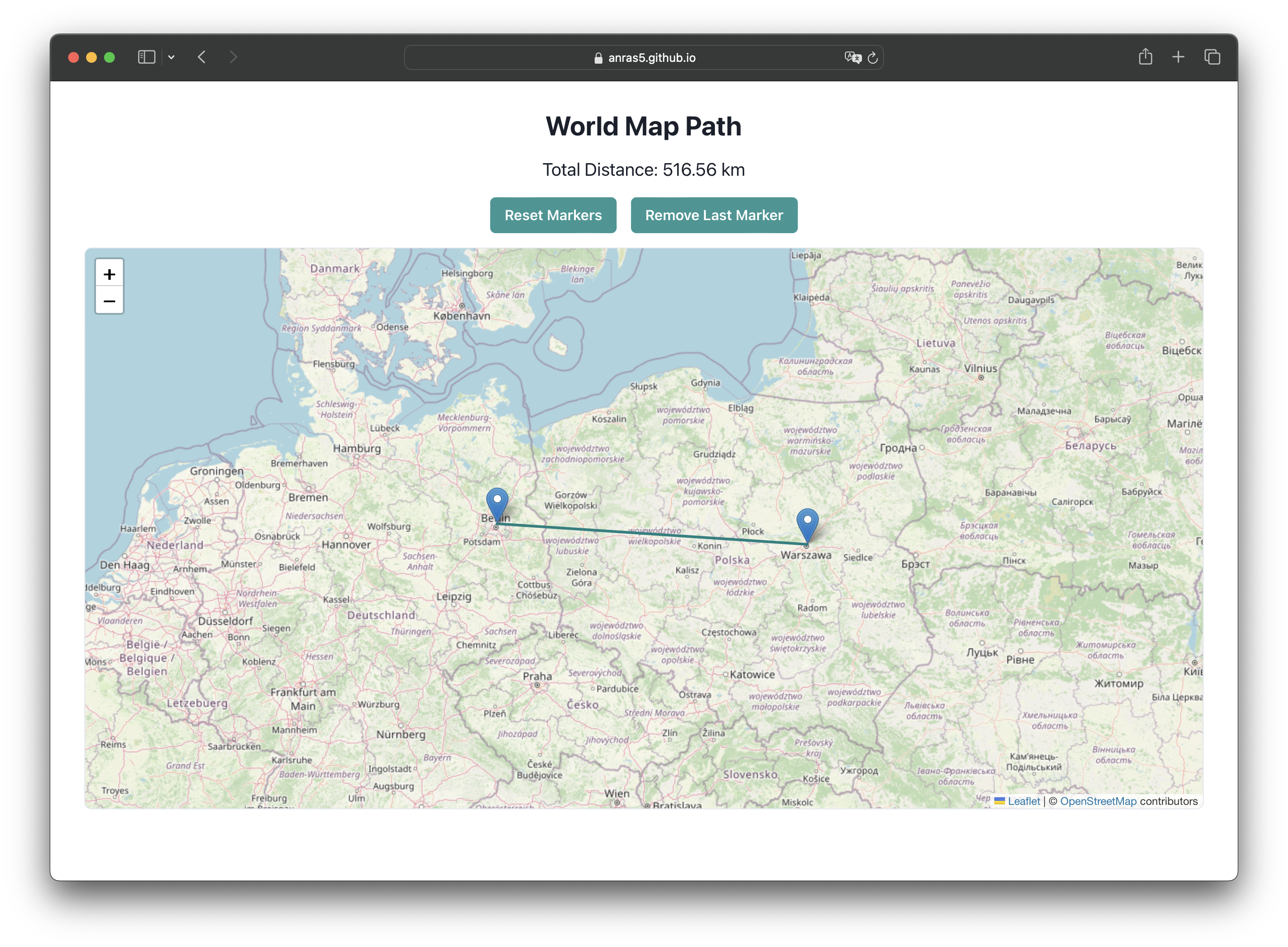
Open terminal and run the following command:
```bash
curl -X POST "<YOUR-URL-HERE>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"points": [[52.520008, 13.404954], [52.237049, 21.017532]]}'
The response should look like this:
{
"distance": 519108.80957046663
}
The distance is in meters, so it is around 519 km. Looks like the function works correctly! 🎉
Cleaning up
If you want to remove the function from Digital Ocean, you can do it by running the following command:
doctl serverless undeploy world-map-path/distance
Conclusion
- We have learned how to create a simple serverless function in Python using Digital Ocean Serverless Functions.
- We tested the function using
cURL. - Digital Ocean Serverless Functions can be very useful when you want use a library that is not available in your programming language but would like to use it. It allows you to create a simple and short program to call from another one.